The financial industry is in the midst of a transformation process, driven by increasing digitization and regulatory pressure and is moving in a very competitive environment where the adoption of an Open Banking model seems essential to be able to offer a customer experience that meets the demands of consumers and allows to face threats from new competitors.
Open Banking is a philosophy that seeks to liberalize the processing of consumers' banking data, so that it can be processed by third parties with the consent of the data subjects.
Its main objective is to favor banking innovation and the development of new products and services, increasing competition in the banking market, facilitating the participation of new players and allowing consumers to exercise control over their own financial data, being able to select with whom they share their data and for what purpose.
Banks lose their monopoly over their customers' data, and must face competition from new entrants, but in return they can increase the value offering and increase the efficiency of their processes.
The concept of Open Banking is leveraged:
- In the creation of the figure of the Third Party Provider (TPP) as a market player that can provide payment services without maintaining the customer's bank account.
- In the use of APIs as a communication protocol between applications that expose and give third parties access to the publishing entity's data architecture.
Entities, both financial and non-financial, can drive new business models or grow existing ones by seeking a better customer experience, expanding the range of products and services or expanding the markets in which they operate.
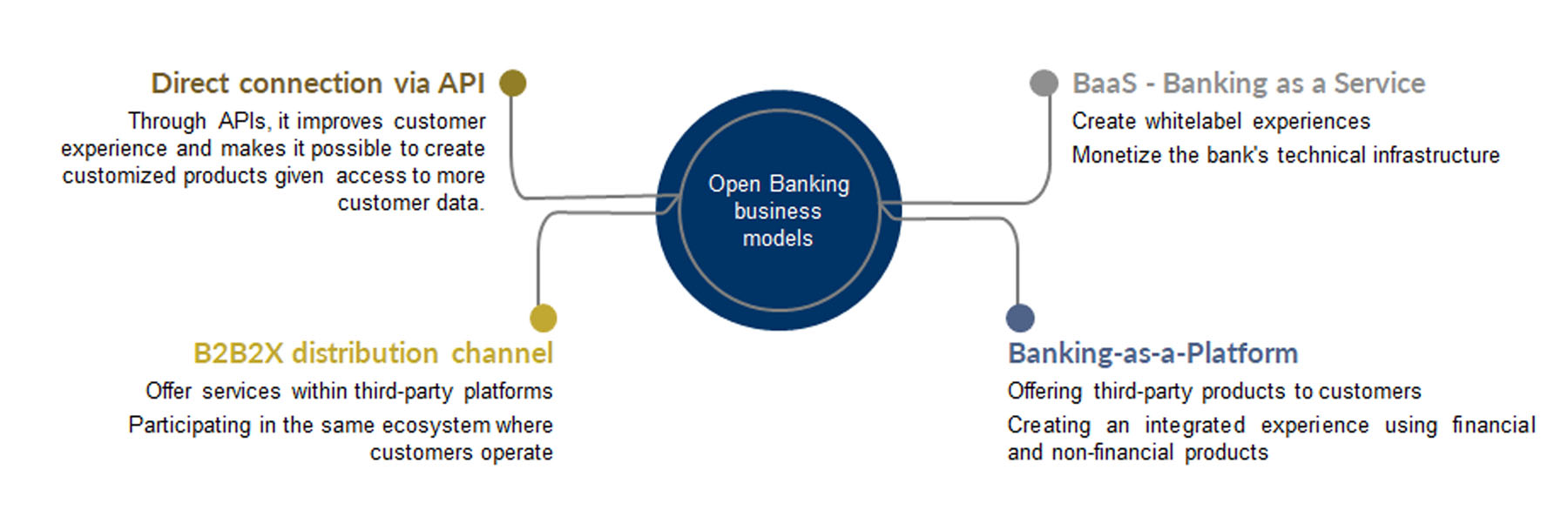
The Open Banking, allows through the use of APIs:
- Capture information from other "competing" entities to personalize product and service offerings and detect cross-selling opportunities.
- Prevent access by uncontrolled third parties.
- Offer new channels for more efficient integration than host-to-host connections.
Additionally enable alternative business models:
- Banking as a Service where a financial institution can offer its financial services as a white label, offering them under the own brand of another institution, which acts as a "virtual" bank, so as to monetize investments in infrastructure, obtain a profit for providing financial services to third parties and take advantage of economies of scale.
- Banking-as-a-Platform where a financial entity makes its platform available for third-party entities to offer their products and services to their own customers, thus increasing their catalog by seeking to cover additional needs that, either by their nature, complexity or need for investment, would not be developed internally.
Open Banking is the result of a drive by regulators to increase competition and transparency in the banking sector and therefore, many countries have implemented or are in the process of developing Open Banking models.
For more information see the full document.